What is Hyper V Windows 10? How does Hyper-V work? If you’re new to Microsoft Hyper-V, it can be quite a challenge to become familiar with the platform, why it’s used, and how it works. This is the start of a series of articles to help you get set with some foundational knowledge around Microsoft Hyper-V.
Let’s start off with exploring some of the basics to give you some background info on what Microsoft Hyper-V is and what you should know to get started.
What is Hyper V Windows 10?
When Microsoft Hyper-V debuted in 2008, virtualization was just beginning to become mainstream. Not many people knew what it was, and even fewer understood what they could do with it. It all seemed conceptually complicated, risky, and challenging to implement and maintain.
A lot has changed in only a little time. Now, virtualization is everywhere. Data centers are built around it. Developers rely on it. Cloud providers depend on it.
Microsoft’s product has been advancing along with the growing interest. Microsoft Hyper-V has been widely adopted and is rapidly gaining on VMware ESXi, arguably the market leader in enterprise virtualization.
If you’ve been waiting for this technology to become more accessible and mature before jumping in, now is the time.
Why Should I Use Microsoft Hyper-V and how does it work?
Moving away from physical hardware and onto Microsoft Hyper-V’s virtualization platform provides a number of benefits. Of course, you have a choice in hypervisors. Microsoft’s primary competitor in the virtualization space is VMware, whose standalone ESXi product is very similar to Hyper-V. There are many Hyper-V vs. VMware debates and comparisons available.
Each vendor offers additional products above and beyond the base product, notably System Center from Microsoft and vSphere from VMware. These two product suites differ quite radically in most metrics and are difficult to compare directly. Here are a few noteworthy items where Hyper-V is the clear winner:
All features are included in Hyper-V Server (the free Microsoft Hyper-V solution)
- Same limitations on virtual machines as Windows Server Datacenter Edition
- Clustering support
- Replica
- Storage on Fibre Channel, NFS, and/or iSCSI with MPIO and/or SMB 3 with multi-channel
- Migration of running virtual machines; even outside and across clusters
Familiar Windows interfaces
Seamless integration with existing Windows Server management tools
Full support for guest clusters
Full support for SR-IOV network adapters, including Live Migration
Hyper-V Replication is also an integral feature of the Hyper-V Role
For purposes of this article, we will focus on the general benefits of virtualization and highlight the particular features that are found in Windows Server with the Hyper-V role or with the free Hyper-V Server.
How does Hyper-V work?
If you’re completely new to this technology, it would help you to take a few minutes to become grounded in the basic concepts of virtualization before diving into Hyper-V. Not having a basic idea of Hyper-V’s operation can lead to conceptual hurdles that prevent successful implementation and operation.
We’ll begin with the familiar computer. You start with the hardware. This is made of the motherboard and the CPU and the memory and the hard drive and the monitor. An operating system is the first layer of software that gets installed. Its primary job is to corral all that hardware, ensuring that all the bits get where they need to go. Part of its function is accepting input from devices such as the keyboard and mouse devices. A related job is directing output to the screen, printers, and other devices.
Whether you know it or not, virtualization is occurring in the above diagram. “Virtualization” is really just another word for “abstraction”. Abstraction is one of the basic functions of an operating system.
You haven’t got the time to learn how to send binary commands and data to the CPU in order to make your printer produce a report. So, the operating system presents to you an abstraction of the printer that you can send print jobs to. The print job that you built was created inside another program that provided an abstraction of the document. The icons and the mouse cursor are abstractions.
A hypervisor takes this abstraction up one more level. This is reflected in the origin of the word. In earlier times, what we now call “operating systems” used to be called “supervisors”. In common Western vernacular, the prefix “hyper-” has come to mean “above super-“. So, the term “hypervisor” was coined to indicate a supervisor of supervisors. Conceptually, it looks like this:
We still have all the same abstractions as in a regular computer system, but now Hyper-V presents another layer between the operating system you’re used to and the hardware. This additional layer allows for multiple operating systems to run on the same hardware.
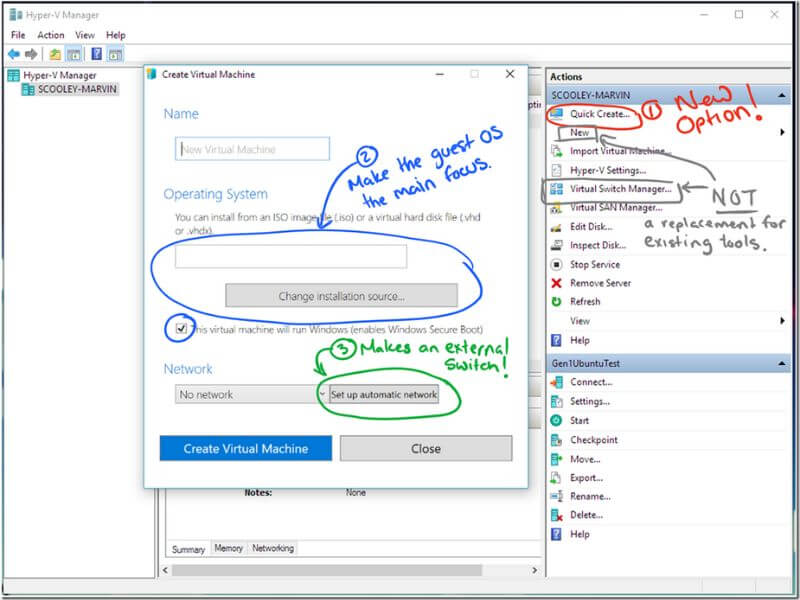
Why Should I Use Hyper-V on the Desktop?
Beginning with Windows 8, and now with Hyper-V Windows 10 & 11, Hyper-V is a built-in component of the Professional and Enterprise editions of the Windows desktop operating system. This offering is a subset of the server-based Microsoft Hyper-V technology. To differentiate the two, the desktop version is called “Client Hyper-V”. It has the following limitations:
- Requires Second-Level Address Translation (SLAT); Hyper-V Server only recommends it
- No clustering or replication
- No migrations (can export and import)
- No SR-IOV support
- No virtual Fibre Channel (can still use FC-attached storage)
- No RemoteFX
Client Hyper-V has one very important distinction among desktop hypervisors: it is a type 1 hypervisor whereas almost all others are type 2. A type 2 hypervisor is just an application that runs inside an operating system and is subjected to the same treatment as other applications, like Microsoft Outlook or a video game.
The root operating system decides when the type 2 hypervisor will be allowed to access resources, which it can then redistribute to guest operating systems.
This often results in very uneven performance for both the root operating system and the type 2 hypervisor’s guests. When Hyper-V Windows 10 or 11 are installed in the client operating systems, Microsoft instantiates and controls the host operating system through Hyper-V, instead of the other way around, transferring the host Windows operating system into a management operating system (explained below). The operations of Hyper-V as a type 1 hypervisor will be explained in the next section.
For your purposes, Client Hyper-V provides a much smoother performance profile than most competing desktop hypervisors. It also comes as a free, built-in component that requires no downloads, purchases, or separate update processes.
Microsoft has embraced the use of Client Hyper-V for other purposes, such as security, in the latest versions of Windows 10 & 11. In Windows 10 & 11, Microsoft leverages client-side virtualization technologies made possible by Hyper-V to instantiate Hypervisor-protected code integrity (HVCI). HVCI provides many security benefits, including:
- Credential Guard
- Protects against modification of Control Flow Guard protection
- Ensures trusted processes like Credential Guard are protected from tampering
- Device drivers run in a protected space that helps shield these from tampering
Above is information about What is Hyper V Windows 10? How does Hyper-V work? that we have compiled. Hopefully, through the above content, you have a more detailed understanding of Hyper V Windows 10. Thank you for reading our post.